LukasKorsikaDesignStudy
From CSSEMediaWiki
(Difference between revisions)
(Fixed layou) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Initial Design == | == Initial Design == | ||
''(converted to Java from C, so some liberties have been taken with classes, but this is essentially its original form)'' | ''(converted to Java from C, so some liberties have been taken with classes, but this is essentially its original form)'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[image:Lko15-OldUML.png]] | ||
=== Design Description === | === Design Description === | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
I realise that this is terrible design. This design study will iteratively improve the design, as well as creating a Java implementation of the program. | I realise that this is terrible design. This design study will iteratively improve the design, as well as creating a Java implementation of the program. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 03:38, 29 July 2010
Contents |
The Problem
The project I design in this study is an application to help me manage my file system. I tend to have a number of copies of the same file scattered throughout my various file system for reasons such as:
- Some partitions are only accessible under Linux
- I often copy videos to my laptop to watch away from my desk.
Requirements
- Must take a list of files as input, and output identical files in groups (ie, cluster all identical files together, don't output unique files)
- Must support a variety of approaches for determining equality -- based on raw data, or file-type specific comparisons.
- Must use reasonable amounts of memory and I/O bandwidth.
- Should be file-system agnostic (and support NFS, etc)
- Should be extensible
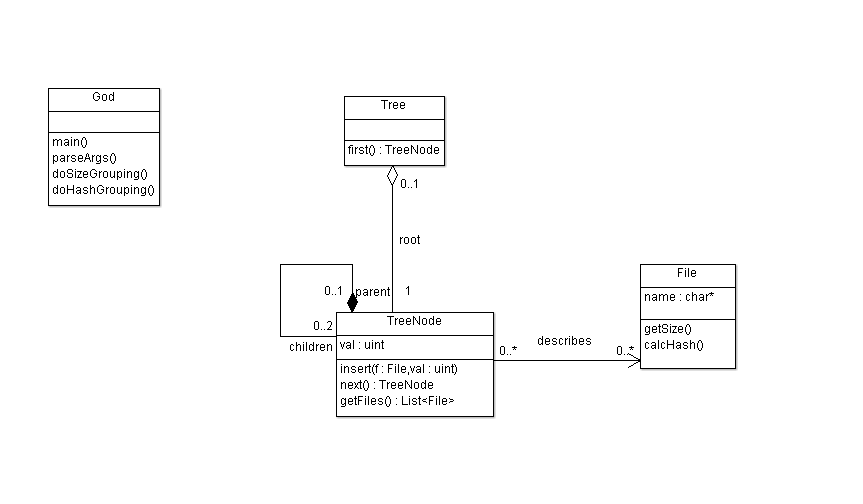
Initial Design
(converted to Java from C, so some liberties have been taken with classes, but this is essentially its original form)
Design Description
As this was a program in C, there is essentially a God Class, with a few helper classes and methods thereupon. The helper classes are:
- File -- This represents a file on the file system, and has methods to find its size, and its SHA-1 hash.
- Tree -- This is a simple class representing a Tree. A tree is composed of a set of TreeNode, and stores a reference to the root.
- TreeNode -- A tree node represents a node in a binary tree, stores its key (which may be size or hash depending on the tree), and a list of all files which have that value. TreeNode has a number of recursive methods to iterate over the tree, get the list of files at that node, and insert a new file with a key recursively.
I realise that this is terrible design. This design study will iteratively improve the design, as well as creating a Java implementation of the program.